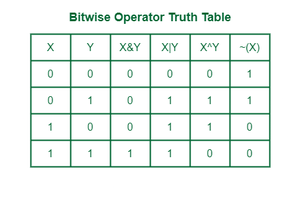
Bitwise Operations are always faster that the arithmetic operations
- AND - &
- OR - |
- NOT - ~
- XOR - ^
- Left Shift - <<
- Right Shift - >>
public class bitwiseOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
int b = 4;
System.out.println("a & b = " + (a & b));
System.out.println("a | b = " + (a | b));
System.out.println("a ^ b = " + (a ^ b));
System.out.println("~a = " + ~a);
System.out.println("a << 1 = " + (a << 1));
System.out.println("a >> 1 = " + (a >> 1));
}
}If the last bit is 1 then the number is odd, otherwise even.
____1&1=1 odd
____0&1=0 even
if(num%2==0){
System.out.println("Number is Even")
}
else{
System.out.println("Number is Odd")
}if(num&1==0){
System.out.println("Even")
}
else{
System.out.println("Odd")
}Given an integer n, return an array ans of length n + 1 such that for each i (0 <= i <= n), ans[i] is the number of 1's in the binary representation of i.
Input: n = 5
Output: [0,1,1,2,1,2]
Explanation:
0 --> 0
1 --> 1
2 --> 10
3 --> 11
4 --> 100
5 --> 101
class Solution {
public int count(int n){
int c = 0;
while(n>0){
int lastbit = n&1;
if(lastbit ==1){
c++;
}
n= n >> 1;
}
return c;
}
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] arr = new int[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
arr[i]= count(i);
}
return arr;
}
}